What are neurotransmitters and what do they do?
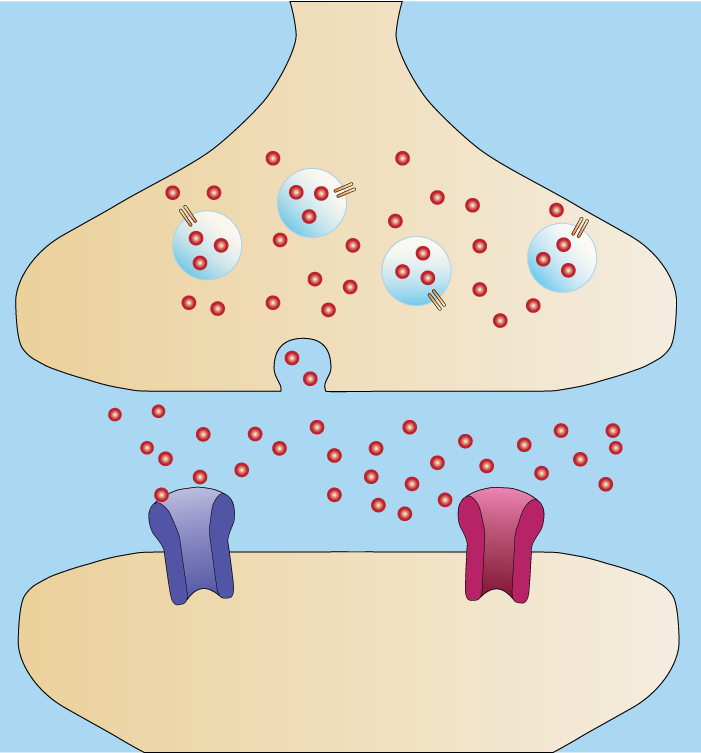
Neurotransmitters are the brain's chemical messengers. They help the brain function correctly, which then allows it to control the many different functions of the body – tissues, glands, organs, and muscles are all affected by neurotransmitters.
Why should you care about your neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters play a vital role in our lives. Our brains use neurotransmitters to tell our hearts to beat, our lungs to breathe, and our stomachs to digest our food. They can also affect our moods, the quality of our sleep, and our ability to focus. If our neurotransmitters become unbalanced, a variety of different symptoms can develop that lead to adverse effects on our bodies over time.
Imbalances in neurotransmitters can lead to:
- Loss of mental focus which is associated with ADHD
- Brain fog
- Addiction and dependency
- Adrenal dysfunction, leading to fatigue and insomnia
- Hormone imbalances
- Insulin resistance
- Mood disorders such as depression and anxiety
- and many more symptoms
Neurotransmitters and their roles in your body
Serotonin – Considered to be the master neurotransmitter, Serotonin regulates many processes, such as our sleep cycle and digestion. Low levels are not uncommon in people on prolonged SSRI use, as over time, SSRIs deplete serotonin from platelets. (1). When serotonin is present in high amounts, it may indicate food allergies, low vitamin D levels, and the use of medications or supplements such as 5HTP. (2)
GABA – This neurotransmitter is often referred to as “nature’s Valium” because it is a very effective mood modulator. It also plays a significant role in balancing the other neurotransmitters in the brain and regulating the amounts of each that are present at a given time. High levels of GABA can lead to feelings of sedation, while low levels are associated with adrenal distress.
Dopamine – Dopamine is our primary “focus” neurotransmitter, and it is largely responsible for regulating our pleasure/reward pathway, memory, and motor control functions. When dopamine is either too high or too low, it contributes to memory problems and an inability to stay on task. Elevated dopamine levels can also contribute to anxiety and hyperactivity, as well as general mood swings and attention disorders.
Norepinephrine – This neurotransmitter is responsible for our ability to pay attention and stay focused. It is produced by the adrenal medulla or synthesized from dopamine, and it plays a critical role in our survival. Norepinephrine is a relay messenger between our brains and nervous systems during the “fight or flight” response, and it also helps our brains make sense of and respond to stimuli from our environment in all situations. High levels of norepinephrine have been linked to anxiety, high blood pressure, and hyperactivity. Low levels have been linked to a lack of energy, motivation, and the inability to focus.
Epinephrine – Epinephrine is synthesized from norepinephrine and is a neurotransmitter that helps regulate essential bodily functions like our metabolism, heart rate, and blood pressure. During the “fight or flight” response, epinephrine helps boost the supply of oxygen and glucose to our brains and muscle tissues while also suppressing non-emergency processes. High levels of epinephrine are associated with hyperactivity, ADHD, anxiety, and trouble sleeping. Low levels are associated with fatigue, depression, and the inability to recover quickly.
Glutamate – An extremely important neurotransmitter, glutamate is a major mediator of signals in the central nervous system – it is involved in most normal aspects of brain function, including cognition, memory, and learning. Elevated levels of glutamate are commonly linked to panic attacks, anxiety, impulsiveness, and excessive adrenal function. Low levels have been linked to memory loss, depression, sleeplessness, and poor adrenal function.
Neurotransmitters and their effects on the lives of children, teens, and adults
Neurotransmitter levels are intricately tied to all our hormone levels, and vice versa.
Changes in any of our hormone levels (sex, adrenal) can have a marked impact on our neurotransmitter levels, leading to imbalances if the changes are not corrected. At the same time, neurotransmitter imbalances can affect hormone production and function.
Bioactive substances (extra-nutritional elements that typically occur in small quantities in foods and can have physiological and behavioral effects) such as caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine and various medications can also contribute to neurotransmitter depletion by suppressing or stimulating neurotransmitter receptor function. When everything is running smoothly, neurotransmitters work within a natural checks and balances system that keeps the levels of each balanced appropriately.
Take control of your brain health
The first step to managing your neurotransmitter levels is to find out what they are. In order to get your hands on this vital information, you’ll need to have your current neurotransmitter levels tested. Canary Club offers cutting-edge neurotransmitter testing kits that can help you learn more about your current levels, and what they mean for your continued health and vitality. Our neurotransmitter tests have optional hormone add-ons so your health practitioner can see a more complete picture. T.
 Once you have more information about your current neurotransmitter levels, you can visit your health practitioner and discuss your results with them. It’s important to keep your doctor in the loop because they may be able to shed some light on your results and help you interpret and apply them to your daily life.
Once you have more information about your current neurotransmitter levels, you can visit your health practitioner and discuss your results with them. It’s important to keep your doctor in the loop because they may be able to shed some light on your results and help you interpret and apply them to your daily life.
We advocate including a health practitioner in the maintenance and balancing of your neurotransmitters. Some imbalances can be corrected without any medications, only requiring dietary supplementation and lifestyle changes. Others may require medical intervention to correct, and this determination is best left to a qualified medical professional, though we always advocate finding a health practitioner who will listen to and respect your wishes concerning your treatment.
Influencing Neurotransmitter Balance
Which vitamin or supplement you choose to take should depend on the condition you have—a deficiency in one area will require different supplementation than an excess in another. This is an area where the advice of a doctor or alternative health practitioner would be very beneficial; you should choose someone who is familiar with natural therapies and is comfortable working with you to balance and maintain your neurotransmitter using vitamins and supplements. As always, when managing your healthcare, be cautious and well-informed.
Diet
Some experts believe that diet can have a great impact on neurotransmitter health. Conditions such as ADHD have received a lot of attention because of the high rate of diagnosis in children, and the wish of many parents and caregivers to avoid the use of medications to treat it. Dietary recommendations are going to depend on the symptoms you are experiencing.
Whatever symptoms you may have, a change in diet can almost always help you feel better. Some foods are said to help aid neurotransmitter and hormone balancing, and eating in a more healthy way is always a good idea.
Exercise
Getting up and moving your body is a proven therapy for many different conditions, including anxiety and depression, which are common symptoms of a neurotransmitter imbalance.
What sorts of activities you undertake should depend on your general fitness level and symptoms, and take into account any limitations you may have. Someone with poor joints should probably steer clear of high-impact routines and work more with low-impact therapies like water-aerobics and yoga.
The goal of exercise as a therapy solution is to stimulate your body and encourage it to function normally. Exercise is said to increase the concentration of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, including serotonin and norepinephrine, which are found in low concentration in individuals suffering from depression. Exercise also affects the brain through the release of endorphins, which can create a temporary elevated mood state.
Your Hormone Management Testing Plan
- Step 1: Start by selecting and ordering your desired test(s). You will receive an at-home testing kit that fits your unique concerns and needs. No prescription or visit to the doctor’s office is required. Your test kit is delivered directly to your front door.
- Step 2: Take the test to establish the starting hormone baseline at the beginning of your plan. Consider developing your plan alongside:
- a licensed health care provider for medical conditions, especially for severe "out of normal range" results
- or a Health Care Coach for nutrition and supplements that will support your desired results
- Step 3: Develop a plan based on your hormone test results, establishing a one-year or more outlook.
- Keep logs of your intakes, and daily routines related to your hormone test results.
- Keep logs of your intakes, and daily routines related to your hormone test results.
- Step 4: After 6-12 months of actively working on your plan, take the same test again to determine your progress.
ZRT Neurotransmitters Profile
 See our ZRT Neurotransmitters Profile to check your neurotransmitter levels. Samples are taken from dried urine, with the exception of the saliva steroids add-on option.
See our ZRT Neurotransmitters Profile to check your neurotransmitter levels. Samples are taken from dried urine, with the exception of the saliva steroids add-on option.
Neurotransmitters Test Kit Includes:
Neurotransmitters Dried Urine: GABA, Glu, Gly, DA, Epi, NE, HIST, 5-HT, PEA, DOPAC, HVA, 5-HIAA, NMN, VMA, Trp, Kyn, 3-OHKyn, Tau, Gln, His, N-MeHist, Tyra, KynAc, Xanth, Tyr, Crtn
Available Neurotransmitter Add-ons:
You will be able to include these add-ons during the ordering process for the Neurotransmitters Panel.
Neurotransmitters + Saliva Steroids Concerned about hormone imbalances? Use the tube in the Neurotransmitter kit to collect a Saliva sample for Estradiol, Progesterone, Testosterone, DHEA-S & AM Cortisol.
Neurotransmitters + Diurnal Cortisol (UDH) I Don't want to test Melatonin. Add only Free Cortisol & Free Cortisone x4 to the same samples being collected for Neurotransmitters.
Neurotransmitters + Diurnal Cortisol & Melatonin UDH II - For concerns about adrenal or sleep issues, add 4-point Cortisol, Cortisone & Melatonin to the same samples being collected for Neurotransmitters.
Neurotransmitters + Diurnal Cortisol, Melatonin, Norepinephrine & Epinephrine UDH III For concerns about adrenal or sleep, stress issues, add Free Cortisol x 4, Free Cortisone x 4, Melatonin (MT6s) x 4, NE x 4 & Epi x 4 to the same samples being collected for Neurotransmitters.
add 7 Toxic Heavy Metals Urine Elements – $99 – Add tests for Iodine, Bromine, Selenium, Lithium, Arsenic, Cadmium & Mercury
Additional Resources
- Neurotransmitter Fact Sheet
- Neuroendocrine Imbalances and Depression
- Our Emotions Reflect Our Neurotransmitter Hormone Balance
- Why You Might Be Starving Your Brain
- Dopamine and New Year's Resolutions
- Neurotransmitter Disruption and Adrenal Function
- Neurotransmitter Imbalances and Mood Disorders
- Forbes Article
References: (1). Siesser WB, Sachs BD, Ramsey AJ, Sotnikova TD, Beaulieu JM, Zhang X, Caron MG,
Gainetdinov RR: Chronic SSRI treatment exacerbates serotonin deficiency in humanized Tph2 mutant mice. ACS Chem Neurosci 2013;4:84-88.
(2). Spiller RC, Jenkins D, Thornley JP, Hebden JM, Wright T, Skinner M, Neal KR: Increased rectal mucosal enteroendocrine cells, T lymphocytes, and increased gut permeability following acute Campylobacter enteritis and in post-dysenteric irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 2000;47:804-811.
.

